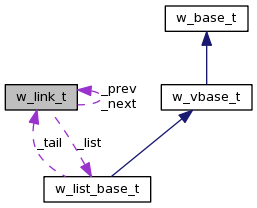

Classes that will always be on one or more lists may contain a member of type w_link_t. This contains the next and prev pointers for putting the class instance into a doubly-linked list.
Embedding the w_link_t structures in the objects to be linked together into a list avoids heap activity for list insertion and removal.
Definition at line 101 of file w_list.h.
Public Member Functions | |
| NORET | w_link_t () |
| NORET | ~w_link_t () |
| NORET | w_link_t (const w_link_t &) |
| w_link_t & | operator= (const w_link_t &) |
| void | attach (w_link_t *prev_link) |
| void | check () |
| w_link_t * | detach () |
| remove containing object from the list. | |
| w_list_base_t * | member_of () const |
| w_link_t * | next () const |
| w_link_t * | prev () const |
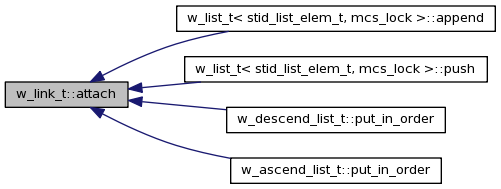
| void w_link_t::attach | ( | w_link_t * | prev_link | ) |
insert object containing this link into the list of which prev_link is a member. Insert after prev_link.
Definition at line 39 of file w_listm.cpp.
References w_list_base_t::_cnt, _list, _next, _prev, and w_assert2.
Referenced by w_list_t< stid_list_elem_t, mcs_lock >::append(), w_list_t< stid_list_elem_t, mcs_lock >::push(), w_descend_list_t< T, LOCK, K >::put_in_order(), and w_ascend_list_t< T, LOCK, K >::put_in_order().
Here is the caller graph for this function:
 1.4.7
1.4.7