



Next: condor_store_cred
Up: 11. Command Reference Manual
Previous: condor_stats
Contents
Index
Subsections
condor_status
Display status of the HTCondor pool
condor_status
[-debug]
[help options]
[query options]
[display options]
[custom options]
[name ... ]
condor_status is a versatile tool that may be used to monitor and query the
HTCondor pool. The condor_status tool can be used to query resource
information, submitter information, checkpoint server information, and daemon
master information. The specific query sent and the resulting information
display is controlled by the query options supplied. Queries and display
formats can also be customized.
The options that may be supplied to condor_status belong to five groups:
- Help options provide information about the condor_status
tool.
- Query options control the content and presentation of status
information.
- Display options control the display of the queried
information.
- Custom options allow the user to customize query and
display information.
- Host options specify specific machines to be queried
At any time, only one help option, one query option and one
custom option may be specified. Any number of custom and host
options may be specified.
- -debug
- Causes debugging information to be sent to
stderr, based on the value of the configuration variable
TOOL_DEBUG
- -help
- (Help option) Display usage information
- -diagnose
- (Help option) Print out query ClassAd without
performing query
- -absent
- (Query option) Query for and display only
absent resources.
- -any
- (Query option) Query all ClassAds and display their type,
target type, and name
- -avail
- (Query option) Query condor_startd ClassAds and identify
resources which are available
- -ckptsrvr
- (Query option) Query condor_ckpt_server ClassAds
and display checkpoint server attributes
- -claimed
- (Query option) Query condor_startd ClassAds and print
information about claimed resources
- -cod
- (Query option) Display only machine ClassAds
that have COD claims. Information displayed includes
the claim ID, the owner of the claim, and the state
of the COD claim.
- -collector
- (Query option) Query condor_collector ClassAds
and display attributes
- -direct hostname
- (Query option) Go directly to
the given host name to get the ClassAds to display.
By default, returns the condor_startd ClassAd.
If -schedd is also given, return the condor_schedd ClassAd
on that host.
- -java
- (Query option) Display only Java-capable resources.
- -license
- (Query option) Display license attributes.
- -master
- (Query option) Query condor_master ClassAds
and display daemon master attributes
- -negotiator
- (Query option) Query condor_negotiator
ClassAds and display attributes
- -pool centralmanagerhostname[:portnumber]
- (Query option) Query the specified central manager using an
optional port number.
condor_status queries the machine specified by the configuration
variable COLLECTOR_HOST by default.
- -run
- (Query option) Display information about machines
currently running jobs.
- -schedd
- (Query option) Query condor_schedd ClassAds and display
attributes
- -server
- (Query option) Query condor_startd ClassAds and
display resource attributes
- -startd
- (Query option) Query condor_startd ClassAds
- -state
- (Query option) Query condor_startd ClassAds and display
resource state information
- -statistics WhichStatistics
- (Query option) Can only be
used if the -direct option has been specified.
Identifies which Statistics attributes to include in the ClassAd.
WhichStatistics is specified using the same syntax as defined
for STATISTICS_TO_PUBLISH. See the definition at
3.3.3 for details.
- -storage
- (Query option) Display attributes of machines
with network storage resources.
- -submitters
- (Query option) Query ClassAds sent by submitters and
display important submitter attributes
- -subsystem type
- (Query option) If type is
one of collector, negotiator, master,
schedd, startd, or quill,
then behavior is the same as the query option without the
-subsystem option. For example,
-subsystem collector is the same as -collector.
A value of type of CkptServer,
Machine, DaemonMaster, or Scheduler
targets that type of ClassAd.
- -vm
- (Query option) Query condor_startd ClassAds,
and display only VM-enabled machines. Information displayed includes
the the machine name, the virtual machine software version,
the state of machine, the virtual machine memory,
and the type of networking.
- -attributes Attr1[,Attr2 ... ]
- (Display option)
Explicitly list the attributes in a comma separated list
which should be displayed when using the -xml or -long
options. Limiting the number of attributes increases the efficiency
of the query.
- -expert
- (Display option) Display shortened error messages
- -long
- (Display option) Display entire ClassAds
(same as -verbose)
- -sort expr
- (Display option) Change the display order
to be based on ascending values of an evaluated expression
given by expr.
Evaluated expressions of a string type are in a case insensitive
alphabetical order.
If multiple -sort arguments appear on the command line,
the primary sort will be on the leftmost one within the command line,
and it is numbered 0.
A secondary sort will be based on the second expression,
and it is numbered 1.
For informational or debugging purposes, the ClassAd output to be
displayed will appear as if the ClassAd had two additional attributes.
CondorStatusSortKeyExpr<N> is the expression,
where <N> is replaced by the number of the sort.
CondorStatusSortKey<N>
gives the result of evaluating the sort expression that is numbered
<N>.
- -total
- (Display option) Display totals only
- -verbose
- (Display option) Display entire ClassAds. Implies
that totals will not be displayed.
- -xml
- (Display option) Display entire ClassAds,
in XML format.
The XML format is fully defined in the reference manual,
obtained from the ClassAds web page, with a link at
http://research.cs.wisc.edu/htcondor/research.html.
- -constraint const
- (Custom option) Add constraint
expression. See section 4.1 and
section 4.1.4 for
details on ClassAds and on writing expressions.
- -format fmt attr
- (Custom option) Display attribute
or expression attr in format fmt.
To display the attribute or expression the format must contain a single
printf(3)-style conversion specifier.
Attributes must be from the resource ClassAd.
Expressions are ClassAd expressions and may
refer to attributes in the resource ClassAd.
If the attribute is not present in a given ClassAd and cannot
be parsed as an expression, then the
format option will be silently skipped.
The conversion specifier must match the type of the
attribute or expression.
%s is suitable for strings such as Name,
%d for integers such as LastHeardFrom,
and %f for floating point numbers such as LoadAvg.
%v identifies the type of the attribute,
and then prints the value in an appropriate format.
%V identifies the type of the attribute,
and then prints the value in an appropriate format as it would
appear in the -long format.
As an example, strings used with %V will have quote marks.
An incorrect format will result in undefined behavior.
Do not use more than one conversion specifier in a given
format. More than one conversion specifier will result
in undefined behavior. To output multiple attributes
repeat the -format option once for each desired
attribute.
Like printf(3)-style formats, one may include other
text that will be reproduced directly.
A format without any conversion specifiers may be specified,
but an attribute is still required.
Include
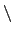 n to specify a line break.
n to specify a line break.
- -autoformat[:tn,lVh] attr1 [attr2 ...]
- (Custom option) Display machine ClassAd attribute values
formatted in a default way according to their attribute types.
This option takes an arbitrary number of attribute names as arguments,
and prints out their values. It is like the -format option,
but no format strings are required.
It is assumed that no attribute names begin with a dash character,
so that the next word that begins with dash is the
start of the next option.
The autoformat option may be followed by a colon character
and formatting qualifiers:
t add a tab character before each field instead of
the default space character,
n add a newline character after each field,
, add a comma character after each field,
l label each field,
V use %V rather than %v for formatting,
h print headings before the first line of output.
The newline and comma characters may not be used together.
- The default output from condor_status is formatted to
be human readable, not script readable.
In an effort to make the output fit within 80 characters,
values in some fields might be truncated.
Furthermore, the HTCondor Project can (and does) change the
formatting of this default output as we see fit.
Therefore, any script that is attempting to parse data from
condor_status is strongly encouraged to use the
-format option (described above).
- The information obtained from condor_startd and condor_schedd
daemons
may sometimes appear to be inconsistent. This is normal since
condor_startd and condor_schedd daemons update the HTCondor
manager at different rates, and since there is a
delay as information propagates through the network and the system.
- Note that the ActivityTime in the Idle state is
not the amount of time that the machine has been idle. See the
section on condor_startd states in the Administrator's Manual
for more information.
- When using condor_status on a pool with SMP machines,
you can either provide the host name, in which case you will
get back information about all slots that are represented on
that host, or you can list specific slots by name.
See the examples below for details.
- If you specify host names, without domains, HTCondor will
automatically try to resolve those host names into fully
qualified host names for you.
This also works when specifying specific nodes of an SMP
machine.
In this case, everything after the ``@'' sign is treated as a
host name and that is what is resolved.
- You can use the -direct option in conjunction with
almost any other set of options.
However, at this time, the only daemon that will allow direct
queries for its ad(s) is the condor_startd.
So, the only options currently not supported with
-direct are -schedd and -master.
Most other options use startd ads for their information, so
they work seamlessly with -direct.
The only other restriction on -direct is that you may
only use 1 -direct option at a time.
If you want to query information directly from multiple hosts,
you must run condor_status multiple times.
- Unless you use the local host name with -direct,
condor_status will still have to contact a collector to find
the address where the specified daemon is listening.
So, using a -pool option in conjunction with
-direct just tells condor_status which collector to
query to find the address of the daemon you want.
The information actually displayed will still be retrieved
directly from the daemon you specified as the argument to
-direct.
Example 1 To view information from all nodes of an SMP
machine, use only the host name.
For example, if you had a 4-CPU machine, named
vulture.cs.wisc.edu, you might see
% condor_status vulture
Name OpSys Arch State Activity LoadAv Mem ActvtyTime
slot1@vulture.cs.w LINUX INTEL Claimed Busy 1.050 512 0+01:47:42
slot2@vulture.cs.w LINUX INTEL Claimed Busy 1.000 512 0+01:48:19
slot3@vulture.cs.w LINUX INTEL Unclaimed Idle 0.070 512 1+11:05:32
slot4@vulture.cs.w LINUX INTEL Unclaimed Idle 0.000 512 1+11:05:34
Total Owner Claimed Unclaimed Matched Preempting Backfill
INTEL/LINUX 4 0 2 2 0 0 0
Total 4 0 2 2 0 0 0
Example 2 To view information from a specific nodes of an
SMP machine, specify the node directly.
You do this by providing the name of the slot.
This has the form slot#@hostname.
For example:
% condor_status slot3@vulture
Name OpSys Arch State Activity LoadAv Mem ActvtyTime
slot3@vulture.cs.w LINUX INTEL Unclaimed Idle 0.070 512 1+11:10:32
Total Owner Claimed Unclaimed Matched Preempting Backfill
INTEL/LINUX 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
Total 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
Constraint option examples
Further explanation and examples are in section ![[*]](crossref.png) .
.
The Unix command
to use the constraint option to see all machines with the OpSys
of "LINUX":
% condor_status -constraint OpSys==\"LINUX\"
Note that quotation marks must be escaped with the backslash characters
for most shells.
The Windows command to do the same thing:
>condor_status -constraint " OpSys==""LINUX"" "
Note that quotation marks are used to delimit the single argument which
is the expression, and the quotation marks that identify the string
must be escaped by using a set of two double quote marks without
any intervening spaces.
To see all machines that are currently in the Idle state,
the Unix command is
% condor_status -constraint State==\"Idle\"
To see all machines that are bench marked to have a MIPS rating
of more than 750, the Unix command is
% condor_status -constraint 'Mips>750'
-cod option example
The -cod option displays the status of COD
claims within a given HTCondor pool.
Name ID ClaimState TimeInState RemoteUser JobId Keyword
astro.cs.wi COD1 Idle 0+00:00:04 wright
chopin.cs.w COD1 Running 0+00:02:05 wright 3.0 fractgen
chopin.cs.w COD2 Suspended 0+00:10:21 wright 4.0 fractgen
Total Idle Running Suspended Vacating Killing
INTEL/LINUX 3 1 1 1 0 0
Total 3 1 1 1 0 0
-format option example
To display the name and memory attributes of each job ClassAd in a format
that is easily parsable by other tools:
% condor_status -format "%s " Name -format "%d\n" Memory
To do the same with the autoformat option, run
% condor_status -autoformat Name Memory
condor_status will exit with a status value of 0 (zero) upon success,
and it will exit with the value 1 (one) upon failure.
Center for High Throughput Computing, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Copyright © 1990-2013 Center for High Throughput Computing,
Computer Sciences Department,
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI. All Rights Reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
See the HTCondor Version 7.9.6 Manual or
http://research.cs.wisc.edu/htcondor/
for
additional notices.




Next: condor_store_cred
Up: 11. Command Reference Manual
Previous: condor_stats
Contents
Index
htcondor-admin@cs.wisc.edu
![[*]](crossref.png)