The Multi-User Model
The Buffer Manager takes care of

The Minibase server instantiates the shared memory area. This shared memory area contains the buffer pool, lock table, transaction table and the log tail. Varying levels of granularity exist for access to the shared components. Semaphores ( acting as latches ) ensure consistency. On startup, the server executes a restart operation initially, to ensure that the system is a consistent state. The server keeps track of the number of clients in the system and needs to be explicitly shut down. At server shutdown, the buffer pool is flushed to disk, all semaphores and shared memory is destroyed and the database is left in a consistent state.
Every client attaches itself to the shared memory region .i.e. it obtains pointers to the objects in shared memory. The client also instantiates pointers to other global objects which operate in its own space: for example, pointers to the DB object, catalogs, recovery manager and the lock manager.
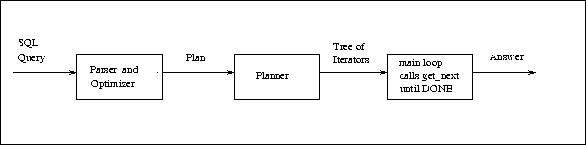
The Query Evaluation
path is identical in both single and multi user versions except
that in the multi user version, log records are written before any
updates to disk, latches and locking is used to maintain the consistency
of the database. During the normal mode of operation, the
RDBMS system merely executes queries from the user.
The RDBMS system functions in the recovery mode when the
system is restarted after a crash.

Next Page of Overview
Click here to go the Minibase Home Page
