CS 779 Spring Semester 2003
Professor Stephen
Chenney
Plan and Goals click to view
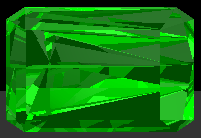
Results : Overall, I was able to render different types of gems quite accurately. To render dispersion effects, I spawned 6 refractive monochromatic rays from the ray that first contacts the diamond surface. The rays then all bounce around inside the diamond, and eventually exit the gem when the angle between the normal and incident ray is less than the critical angle of the gemstone. The light source is basically all the walls around the diamond. I used a ceiling area light source, then ran my radiosity program to transfer light before ray tracing the dispersion. Fresnel values are calculated and multiplied with the spectral color value of the surface. The fresnel equation I used was the same one in our lecture notes this semester. The diamond in the pictures below is colorless (black) before the rendering takes place.
A dispersive
colorless diamond
Dispersive colorless diamond at 45 degree angle along the x and y axes
A colorless diamond without dispersion
I accounted for Volume absorption by using Beer's Law. I looked up the absorption values for different wavelengths of solids in an optics book. As the ray bounces around inside the solid, it's color intensity lowers exponentially. This basically causes an overall darker color of the gemstone and in some slightly changed colors. The examples below show this.
A yellow diamond without absorption.
A yellow diamond with absorption.
I modeled three different types of gemstone cuts, the brilliant cut, the emerald cut, and the marquis cut. Modeling the stones was probably the most tedious and lengthy part of the project. I basically used reference sites for pictures and dimensions of the cuts, and then set up the vertices and triangles in a scene file. I started off the process by placing a vertex at 0,0,0 and called this the middle of the gem table ( the top of the gemstone ). From there, knowing the dimensions and angles of the different types of cuts, I built on more vertices using lots of trig. Below are some pictures showing emeralds and sapphires. The emerald has an emerald cut, and the sapphire has a marquis cut. The bottom surface is reflective just for a cool effect.
Emerald and sapphire top view
Emerald and sapphire side view
Emerald and sapphire facing eachother.
Below are a couple links to pictures showing many of the gemstones I modeled.
Five gems sitting on a reflective surface.
Many gems on a reflective surface.
Dispersive colorless diamond at 45 degree angle along the x and y axes
A colorless diamond without dispersion
I accounted for Volume absorption by using Beer's Law. I looked up the absorption values for different wavelengths of solids in an optics book. As the ray bounces around inside the solid, it's color intensity lowers exponentially. This basically causes an overall darker color of the gemstone and in some slightly changed colors. The examples below show this.
A yellow diamond without absorption.
A yellow diamond with absorption.
I modeled three different types of gemstone cuts, the brilliant cut, the emerald cut, and the marquis cut. Modeling the stones was probably the most tedious and lengthy part of the project. I basically used reference sites for pictures and dimensions of the cuts, and then set up the vertices and triangles in a scene file. I started off the process by placing a vertex at 0,0,0 and called this the middle of the gem table ( the top of the gemstone ). From there, knowing the dimensions and angles of the different types of cuts, I built on more vertices using lots of trig. Below are some pictures showing emeralds and sapphires. The emerald has an emerald cut, and the sapphire has a marquis cut. The bottom surface is reflective just for a cool effect.
Emerald and sapphire top view
Emerald and sapphire side view
Emerald and sapphire facing eachother.
Below are a couple links to pictures showing many of the gemstones I modeled.
Five gems sitting on a reflective surface.
Many gems on a reflective surface.