Heapfiles
Introduction
A heapfile is an unordered set of variable sized records. Each record
is viewed as a sequence of bytes. The heapfile component of Minirel
provides the ability to create heapfiles and to open existing ones.
Records can be inserted to and deleted from the heapfile. Each record
has a unique record identifier. By specifying the record id, a
specific record can be retrieved or updated in place. Sequential
scans on the heapfile are supported. Finally, heapfiles can be
deleted from the database.
The heapfile component uses the buffer manager to read and write
pages. It also directly accesses the directory service offered by the
space manager. The methods provided the lock manager are used for
regulating the accesses by concurrent users of the heapfile. Crash
recovery is ensured through the physical logging of updates to pages,
using the recovery manager.
External Interface
The heapfile component exports the classes HeapFile and
Scan.
Class HeapFile
class HeapFile
{
friend class Scan;
public:
HeapFile(char* name,Status& returnStatus);
~HeapFile();
Status insertRecord(char* recPtr, int recLen,
RID& outRid);
Status deleteRecord(const RID& rid);
Status updateRecord(const RID& rid, char* recPtr,
int reclen);
int getRecCnt();
Status getRecord(const RID& rid, char* recPtr,
int& recLen);
Scan* openScan(Status& status);
Status deleteFile();
}
The class HeapFile provides the abstraction of an unordered set
of records. The records are a sequence of bytes and no field structure
is assumed. The methods return a status that indicates whether the
operation was successful or not (refer global_error).
The constructor takes the name as an input parameter. If a heapfile
with the name already exists in the database, it is opened. If not, a
heapfile is created with this name. The destructor closes the
heapfile.
Each record in the heapfile has a unique identifier of type RID.
insertRecord() inserts the specified record into the heapfile and
returns the rid corresponding to the record. deleteRecord()
takes the record identifier and deletes the corresponding record from
the heapfile. If the specified record identifier does not correspond
to an actual record, an error is flagged. The method
updateRecord() modifies the contents of the specified record without
changing its rid. In the current implementation, there is a
restriction that the length of the new record should not exceed that
of the old record.
getRecCnt() returns the number of records that are currently
stored in the heapfile. A specific record can be retrieved by passing
its record identifier to getRecord(). deleteFile()
removes the heapfile from the database. A sequential scan of the
heapfile can be initiated through openScan(). This method
returns an object of type Scan, which is discussed in the next
section.
Class Scan
class Scan
{
public:
~Scan();
Status getNext(RID& rid, char* recPtr, int& recLen);
}
The Scan class supports the sequential scan of a heapfile. No conditions
can be applied on the scan and thus, all the records in the heapfile
are retrieved in turn. Objects of this type can only be constructed by
openScan() method of the HeapFile class and hence, the
constructor of this class is not public to the users of the heapfile
component.
getNext() fetches the next record in the heapfile. It also
returns the record identifier of the retrieved record. This method
returns DONE when there are no more records to be fetched.
Internal Design
The heapfile is essentially a set of pages in the database on which a
special structure is imposed. When a heapfile is created, a header
page is allocated and the file entry consisting of the name and the
identifier of the header page is inserted into the directory using a
method of the DB class. When the constructor of the heapfile is
invoked, it is determined whether the heapfile is to be created or
just opened. This is done by using the get_file_entry() method
of the DB class. If the entry with the specified name does not exist
in the directory, the heapfile is created. Otherwise it simply opens
the heapfile.
The header page of the heapfile is different from the other pages of
the heapfile. The header page does not store any records. The
structure of the header page is as follows.
struct HeaderPage
{
char fileName[MAX_NAME]; // name of file
PageId firstPage; // pageNo of first data page
PageId lastPage; // pageNo of last data page
int pageCnt; // number of pages
int recCnt; // record count
};
The firstPage and lastPage fields are used in the method
for inserting records.
Each of the data pages of the heapfile share a common structure. The
class HFPage provides the abstraction for a data page of the
heapfile.
// slot structure
struct slot_t {
short offset;
short length; // equals -1 if slot is not in use
};
const int DPFIXED= sizeof(lsn_t)+sizeof(slot_t)+4*sizeof(short)+
3*sizeof(int);
const int DATASIZE = PAGESIZE - sizeof(lsn_t);
class HFPage {
private:
char data[DATASIZE - DPFIXED];
slot_t slot[1]; // first element of slot array
short slotCnt; // number of slots in use;
short freePtr; // offset of first free byte in data[]
short freeSpace; // number of bytes free in data[]
short dummy; // for alignment purposes
PageId prevPage; // backward pointer to data page
PageId nextPage; // forward pointer to data page
PageId curPage; // page number of current pointer
public:
void init(PageId pageNo); // initialize a new page
void dumpPage(); // dump contents of a page
PageId getNextPage(); // returns value of nextPage
PageId getPrevPage(); // returns value of prevPage
void setNextPage(PageId pageNo); // sets value of nextPage
void setPrevPage(PageId pageNo); // sets value of prevPage
// inserts a new record pointed to by recPtr with length
// recLen onto the page, returns RID of record
Status insertRecord(char* recPtr, int recLen, RID& rid);
// delete the record with the specified rid
Status deleteRecord(const RID& rid);
// returns RID of first record on page
// returns NORECORDS if page contains no records.
// Else, returns OK
Status firstRecord(RID& firstRid);
// returns RID of next record on the page
// returns ENDOFPAGE if no more records exist on the page
Status nextRecord (RID curRid, RID& nextRid);
// copies out record with RID rid into recPtr
Status getRecord(RID rid, char* recPtr, int& recLen);
// returns a pointer to the record with RID rid
Status returnRecord(RID rid, char*& recPtr, int& recLen);
}
Slot Directory Structure
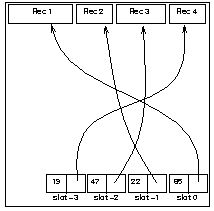
The HFPage class uses a slotted page approach for organizing
variable sized records. The records are stored one after another
starting at byte 0 of the page while the slot array grows from the
rear of the page towards the front. As the records are deleted, the
resulting hole is compacted. However, since records are addressed via
a RID (consisting of the pair), the slot array is not
compacted. Each element of the slot array contains the offset into the
page where the record starts and its length. If the slot is not in
use, the length field is set to -1. The slots in the array are
themselves numbered as 0,-1,-2 and so on. Thus the slot number
specified in a RID has to be inverted before indexing into the
array. slotCnt is used to indicate the current end of the slot array.
freePtr is the first free byte in data[] and freeSpace keeps track of
how much free space is available in data[]. dummy is needed for
alignment. The nextPage and prevPage attributes are used to form a
doubly linked list of the pages in the heapfile.
The methods of HFPage provide the primitives for all operations on
a single page. insertRecord() tries to insert the specified
record into the page. It returns a error if there is not sufficient
free space on the page. deleteRecord() deletes the specified
record and compacts the hole created. This requires that all the
offsets in the slot array, of all the records to the right of the hole
be adjusted by the size of the hole. firstRecord() and
nextRecord() are used to fetch records off a page. The
getRecord() method copies out the specified record, while the
returnRecord() method returns a pointer to the record. The latter
function is used by the updateRecord method of HeapFile.
The methods in the HeapFile class invoke suitable methods of the
HFPage class. insertRecord first determines the page where the
record insertion is attempted. In the current implementation, the last
page of the heapfile is the only page considered for insertion. If
there is not enough space on the last page, a new page is created and
the record inserted there. An alternative implementation could involve
maintaining a list of pages that have some free space in
them. However, due to variable sized records, this strategy might
degenerate to an entire scan on insert, in the worst case.
deleteRecord() simply calls the function with the same name on the
appropriate data page. updateRecord() first obtains a pointer to
the record on the page and then modifies its contents.
deleteFile() deallocates the pages belonging to the heapfile and also
deletes the file entry from the directory.
openScan() returns a Scan object. The Scan class maintains the
RID of the last record that has been returned by it. Thus a call to
getNext() searches for the record following the current rid and
returns it. If no such record is found i.e. the last record on the
last page has already been returned, the scan is done.
The page level locking primitives provided by the lock manager are
used for concurrency control. A page that is read is locked in the
shared mode and any that is modified is locked in exclusive mode. A
finer granularity of locking could have improved the concurrency of
operations on the heapfile immensely.
Updates to pages belonging to the heapfile are logged using the method
provided by the recovery manager. Physical logging is performed and
the before and after images of the affected portions of the page are
logged.
Ravi Murthy
Sriram Narasimhan


